Introduction
Reem Al-Ansary, Vice President of Total Quality Management at ITWorx was heading to her office in ITWorx Free-Zone premises in Cairo, Egypt. It was June 2010, and she had just finished an internal quarterly review meeting with her team. This was a regular meeting held at the end of each quarter to discuss the progress in the Top Suppliers program and to prepare for the client review meeting which was attended by representatives from all business units of the Fortune 50 Company1.
1 The name of the company was removed and the name of the certification program was altered for confidentiality.
Reem has been with the company for around 11 years. She was promoted to Vice President of Total Quality Management in 2006. She leads the Quality Division, which was established in 2000, spanning testing, quality assurance, process improvement, and organizational performance. In addition, she also led quality standard initiatives like CMMI and ISO2.
2 See Glossary for information about the terms.
By the end of 2008, the Fortune 50 Company initiated a new requirement for all of its suppliers to comply with its Top Suppliers program in order to remain on its list of preferred suppliers. By the start of 2009, Wael Amin, ITWorx President, assigned Reem to start a new initiative to drive the Top Suppliers certification compliance for the account. ITWorx needed to pass the certification assessment before the end of 2010 in order to maintain its contract with the company. In turn, Reem assigned Dahlia Arafa, the Organization Performance Manager, as a project manager to lead this initiative. A lean assessment had to be taken by each supplier to decide about the current performance. Dahlia’s starting point was the gap analysis of the results of the lean assessment. The plan was to leverage the existing internal processes to satisfy the certification requirements.
In the review meeting, it was revealed that of the four categories of the Top Suppliers program; “Quality” and “Delivery” targets were consistently met. The progress of the “Customer Satisfaction” category was good but the target was not met yet. The “Lean Assessment” category targets were still not met and further actions had to be taken. According to the “Top Suppliers” implementation plan, activities related to lean were due to start. Those activities were grouped into two projects focusing on two factors of the lean assessment; 5S and Value Stream Management (VSM).
By the end of the review meeting the team had reviewed the initial projects’ plans, agreed about the objectives and assigned team members for each project. Further actions were needed to detail the plan for the two projects and to start performing the required tasks to get things done on time. The 5S implementation project was to include the whole organization, yet starting with the account of the Fortune 50 Company. To implement VSM, the agreement was to use Six Sigma where the assigned team will be trained, certified (one Black Belt and four Green Belt) and the certification project will focus on VSM.
After finishing the meeting and as she reached her office, Reem was thinking deeply about the odds of getting things done on time for the contract renewal. The current progress was promising but effort is needed to sustain this progress. She was also worried about the outcome of the 5S and Six Sigma projects. The success of those projects was the cornerstone in achieving the remaining targets of the Top Suppliers Program. A lot of work is required by the whole team to allow ITWorx to close the existing gaps and to meet the Top Suppliers program requirements in order to maintain its business with one of its key customers, the Fortune 50 Company.
Organizational Background
ITWorx Company Overview
ITWorx is a professional software services firm in Egypt with more than 700 employees. Headquartered in Cairo, with development centers in Cairo and Alexandria, ITWorx has other offices in the Gulf region, namely the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar, and is represented in both Europe and USA. The company was established in 1994 by two AUC3Computer Science graduates Wael Amin and Ahmed Badr. They founded ITWorx with Youssri Helmy, their third partner. ITWorx mission is:
“To be our stakeholders’ trusted partners and agent of change”
3 AUC – The American University in Cairo
ITWorx is driven by a strong corporate culture – a culture that stems from, and feeds back into, every individual in the company4
4 ITWorx website, http://www.itworx.com/AboutUs/Values/Pages/default.aspx, accessed on 10th of October 2010.
“Everything we do is based on five core values that define who we are, how we perform, and what we aspire to: innovation, integrity, quality, agility, and team-play.”
The company offers Portals, Business Intelligence, Enterprise Application Integration, and Application Development Outsourcing services to Global 2000 companies. Furthermore, ITWorx serves governments, financial services firms, educational institutions, telecommunication operators, and media companies in North America, Europe, and the Middle East. In 2008, ITWorx became privately held, with financial backing from the EuroMena Fund, Venture Capital Bank and Proparco.
ITWorx structure is composed of two primary functions “Professional Services” and “Quality Management” which provide together the business delivery focus. Alongside, there are several supporting functions for HR & Operations, Finance, MIS, Sales and Marketing (Figure 1). Ahmed Badr, Vice President of Professional Services, is the head of the Professional Services department and Reem Al-Ansary, VP of Total Quality Management, is the head of the Quality Management department.
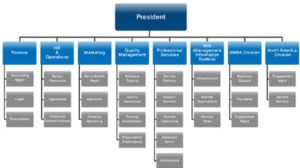
Figure 1 – ITWorx Organization Chart
Standard Quality Initiatives in ITWorx
Since its foundation in 1994, ITWorx considered quality as one of the five core values that built its strong corporate culture. Throughout the years, and in order to align the processes with the core values, ITWorx pursued various standard quality initiatives to ensure quality is built into the core of the provided services. Moreover, ITWorx sought to be certified by both its partners and its customers.
By the end of 2005, ITWorx was ISO certified – certificate 9001:2000 (Exhibit 1) and CMMI level-3 certified. In 2009, ITWorx affirmed its commitment to deliver quality solution by renewing its CMMI level-3 certification (Exhibit 2). In 2010, ITWorx upgraded Quality Management Certificate to ISO 9001:2008. The renewal of those certifications demonstrated ITWorx commitment to continual improvement, and manifested the existence of robust development, maintenance, and project management processes.
As a CMMI Level-3 and ISO 9001:2008 certified organization, ITWorx has demonstrated its ability to consistently provide products and services that meet customer and statutory and regulatory requirements. ITWorx has enhanced customer satisfaction through the effective application of a quality management system, with processes for continual improvement and assurance of conformity.
ITWorx has partnerships with the most influential pioneers and established technology providers in the world (Exhibit 3). For example, ITWorx is a Microsoft Gold Certified Partner. For more than eleven years, ITWorx has been leveraging its relationship with Microsoft to extend customers’ IT organization, augmented with agile, high quality, productive capabilities, technology competences, and vertical industry know-how. ITWorx was awarded the 2007 MS Partner of the Year award for Custom Development Solutions.
Commenting on the award, Wael Amin, President of ITWorx declared5:
“Microsoft trusts ITWorx to deliver world-class business solutions incorporating Microsoft technologies. In turn, ITWorx is committed to quality, innovation, on-time delivery and total customer satisfaction.”
5 Press Release, http://www.itworx.com/News/Press+Releases/ITWorx+Counted+Among+
Top+Finalists+for+the+2007+Microsoft+Partner+of+the+Year+Award+in+Custom+Develo.htm ,
accessed on October 2010.
And commenting on ITWorx partnership, Allison L. Watson, Corporate VP, Microsoft Worldwide Partner Group said5:
“We have a diverse and talented partner ecosystem that each year raises the bar in the design and deployment of customer solutions built on Microsoft technologies. We are pleased to recognize ITWorx as one of our partners leading the field in this category.”
The Fortune 50 Company
The Fortune 50 Company is one of the largest conglomerates of leading high-tech companies in the world with a long history of pioneering innovation in aerospace, aviation, helicopter design, climate control, elevator design and hydrogen fuel cells. The company employs over 206,700 people, operates in more than 180 different countries and is the 37th largest U.S. Corporation.
Since 1995, ITWorx started a long-term strategic partnership with this Fortune 50 Company and hence ITWorx became one of its trusted suppliers for services and key strategic partners. ITWorx offers services like Portals, Business Intelligence, Application Development Outsourcing, and Application Availability Assurance (AAA) support to various business units within the company.
The Top Suppliers Program
Program Initiation
The Fortune 50 Company does business in more than 180 countries and maintains relationships with more than 50,000 suppliers. Its customers expect a strong value proposition, innovative product solutions, perfect quality and on-time delivery. To delight their customers, the Fortune 50 Company uses their customer oriented intellectual operating system to drive improvement in business results and target best in class performance by focusing in closing gaps to achieve results.
The Fortune 50 Company’s ability to achieve perfect quality and on-time delivery depends heavily on supplier performance. So it is crucial that suppliers perform to the highest standards for business practices, environmental responsibility and operational excellence. The company works closely with the suppliers to help them meet increasingly stringent requirements and thereby enable it to deliver superior solutions for customers in the most efficient way, on time and with minimum resources.
In 2008, the Fortune 50 Company established the “Top Suppliers” program to drive supplier performance improvements and to recognize those suppliers with exceptional performance. The Top Suppliers program was mandated by all the company’s Business Units. The suppliers can leverage their own operating system to achieve Top Suppliers results or contact the company for information on its intellectual operating system.
Program Criteria
The Top Suppliers program qualification criteria have four categories: quality, delivery, lean assessment and customer satisfaction (market feedback). The ultimate goal is to have every supplier reaching the highest level of performance, to become a Top Supplier.
The following are the target performance measure for each category; those measures should be maintained for 12 consecutive months.
Quality: zero escapes or best-in-class
- Delivery: 100% on-time delivery or best-in-class
- Customer satisfaction (market feedback): score ≥ 6.0
o Score ≥ 350 for Manufacturing,
o Score ≥ 260 for Services and Distributors.
6 Lean assessments should be in place to ensure continuous improvement is implemented and results are sustainable over the long term.
There are six steps on the Top Suppliers journey. The first step is to measure the current performance and then to conduct a lean assessment. The third step is to obtain market feedback measuring customer satisfaction. Then to develop and to implement a gap closure plan based on the analysis of the lean assessment results and the customer satisfaction score. The fifth step is to measure the effectiveness of the plan by monitoring scorecard metrics. Finally, the Fortune 50 Company validates the results and for those meeting the target criteria, the nomination and award process begins.
The Top Suppliers program is based on lean implementation where the core idea is to maximize customer value while minimizing waste. The ultimate goal of the lean implementation is to provide perfect value to the customer through a perfect value creation process that has minimum waste. The normal steps to achieve lean are to identify the waste in the existing process and eliminate the sources of waste. Those steps are repeated continuously.
ITWorx and Top Suppliers Program
Top Suppliers Initiative in ITWorx
By the end of 2008, ITWorx joined the Top Suppliers program and started to work on the program requirements. This was mandatory in order to remain in the list of preferred suppliers for the Fortune 50 Company. Wael Amin, ITWorx President, assigned Reem Al-Ansary, Vice President of Total Quality Management of ITWorx to start a new initiative to drive the Top Suppliers Certification compliance for the account. The target date to be nominated for Top Suppliers was the end of 2010, which corresponds to the time of contract renewal with the company.
Having the top management endorsement, Reem started forming the implementation team. She assigned Dahlia Arafa, the Organization Performance manager, as a project manager to lead this initiative under her sponsorship. Given the choice between the Fortune 50 Company’s intellectual operating system and ITWorx local existing processes, it was decided to capitalize on ITWorx operating system and leverage the existing processes to satisfy the certification requirements. This would give the team the chance to leverage existing efforts in the other quality initiatives. Although, ISO and CMMI initiatives were implemented throughout the whole company, it was decided that the Top Suppliers initiative would be implemented only in the Fortune 50 Company account. After the implementation in this account is completed, it would be assessed to decide if it could be rolled out to the remaining accounts.
Lean Concepts for Software Services
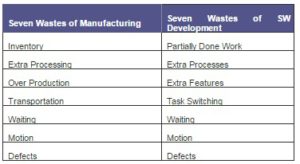
Before starting the Top Suppliers journey, the implementation team needed to map the lean concepts from manufacturing to software services. One step was to map the seven wastes of manufacturing to the corresponding wastes in software development (Table 1).
Table 1 – Wastes in Software Development
The second step was to identify the opportunities for wastes at ITWorx and how to deal with them (Table 2).
Table 2 – Possible Wastes at ITWorx
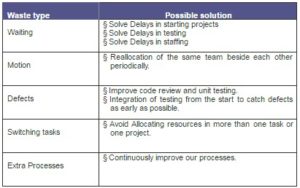
The implementation team also defined possible ways to apply lean concepts in software companies like ITWorx:
- Eliminate un-needed features (implement them in next phases).
- Eliminate absorbed change requests.
- Eliminate finger pointing (between client and vendor).
- Unit testing to eliminate/reduce retesting and bug fixing cycles.
- Replicating client environment on vendor site to eliminate deployment problems.
Top Suppliers Journey in ITWorx
Following the Top Suppliers journey, the first phase was to measure the current performance to identify any performance gaps. The lean assessment was taken and the market feedback was performed through all related customers. The results of the lean assessment and the market feedback were both analyzed to identify the areas that needed improvement. With respect to the four categories of the program, the overall result showed good performance in quality and delivery, while the customer satisfaction needed further improvement. The overall assessment score was 213 compared to the minimum required 260.
The next phase was to develop and implement a gap closure plan by prioritizing opportunities for improvement, translating them into discrete actions and allocating the resources to execute those actions. The team started by putting together a road map of the required actions using a gated approach where the client review is done at the end of each gate before proceeding to the next gate. The third phase was to agree on appropriate metrics definitions and threshold relative to the software services industry.
ITWorx Defined Metrics
Quality
The target for quality was zero escapes or the “best-in-class” over 12-month duration. An escape is a defect passed from the supplier to the client. For ITWorx, this was translated into two types of escapes; major escapes and minor escapes.
Major escapes are defined as incidents that significantly impact product/services provided by ITWorx with major disruption to the Fortune 50 Company customer base and which results in major economic, environmental, health and safety (EH&S), and/or schedule damage requiring immediate corrective action. The required supplier performance is zero escapes or benchmarked as best in class over 12-month duration
Minor escape or turnback is any external problem, other than significant issues captured as internal escapes, that hinders the flow of work. It also can include any inefficiency in the process. The metric used, referred to as minor escapes rate, divides the number of minor escapes from quality clinic process charts (QCPC) tool by the total number of billable hours developed for the Fortune 50 Company, over the last 12 months.
Minor Escapes Rate = Minor Escapes count for 12 months / Total # of billable hours spent in Fortune 50 Company account
ITWorx tracks all billable hours spent per resource per project for the company. This is represented in time sheets that are sent out with monthly invoices and represent hours directly billed to the company as well as overruns due to scope updates or similar that are agreed upon with the company. Non-billable hours, such as internal handover or training hours are ITWorx internal and do not count in the total denominator for the minor escapes rate described above. Benchmarking analysis efforts led to a defect density (Number of minor escapes per hour) of 0.006/hour or less as best in class for this metric. From the gap analysis, the targets for this category were already satisfied for both types of Escapes using the existing processes.
Delivery
The target for delivery was to have 100% on-time delivery (OTD) to the Fortune 50 Company requirements. The missed or hit deliveries were agreed on jointly with the client. ITWorx engagement manager (EM) conducted project end reviews with the customer to agree if a project was delivered on time or missed. The delivery dates were adjusted with scope changes and other change requests and the baseline was updated accordingly. The on-time delivery was then measured against the latest baseline date agreed before the project delivery. It was agreed to have the OTD metric banded as 90-100% on 12 month rolling average. From the gap analysis, the target for this category was already satisfied using the existing processes.
Customer Satisfaction (Market Feedback)
Customer satisfaction was measured using a market feedback form (Figure 2) which was completed by each of the customers (different business units). It had seven-point rating scale, for which there were eight categories. The overall performance (first question) was the dominant question for the Top Suppliers Score. Average score required is 6.0 or higher. The target for this category was not met, and improvement plans needed to be executed to raise the score.
 Figure 2 – Market Feedback Form
Figure 2 – Market Feedback Form
Lean Assessment
The lean assessment was based on the following factors for services (description of those factors can be found in the Glossary):
- Continuous Process Improvement
- Value Stream Management (VSM)
- Relentless Root Cause Analysis (RRCA)
- Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
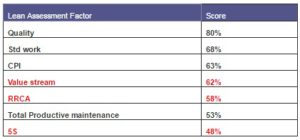
The Top Suppliers program requirement is to have a minimum score of 260 out of possible 347 points. ITWorx initial assessment resulted in a score of 213 which showed that further work was needed in some factors based on the achieved scoring (Table 3).
Table 3 – Possible Wastes at ITWorx
Gap Closure Plan
As shown from the current situation analysis, the required work could be broken down as follows:
- Enhance the existing areas of strength to ensure their sustainability. This would cover both quality and delivery.
- Improve the existing level of customer satisfaction to reach the required score.
- Start new projects to improve the lean assessment score. These projects should focus on areas like 5S and VSM.
The first step started by capitalization over the existing processes to use them to enforce the results obtained in both quality and delivery categories. This step leveraged the companywide activities already preformed for renewing the CMMI level-3 certification which took place in 2009. The implementation team collaborated with the process improvement team and the service delivery team to ensure that the plan for CMMI renewal also covered the Top Suppliers program requirements. Alongside, the efforts to upgrade the ISO certification to ISO 9001:2008 were also leveraged to maintain the targets of both categories. This step was part of the continuous process improvement which was one of the main pillars of Top Suppliers.
The second step started by developing a plan for the Fortune 50 Company account to improve the customer satisfaction index. More emphasis was put on this area by adding the customer satisfaction results to the performance appraisal for the Engagement Managers. This resulted in having more follow-ups with the clients to collect their feedback and resolve any issue, even before they were reported. Furthermore, RRCA techniques like 5-Whys and Fishbone diagram (Figure 3), were formally started by the delivery team to study the root causes of the problems and to ensure they were not repeated. They also closed the loop with the customer to ensure the proposed solutions gained their approval and satisfaction. Once the customer satisfaction improvement plan was completed, the execution started by the delivery team, and it was supported and monitored by the program implementation team.
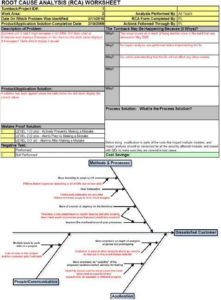 Figure 3 – Rrca Samples Using 5 Whys and Fishbone Techniques
Figure 3 – Rrca Samples Using 5 Whys and Fishbone Techniques
By June 2010, ITWorx had renewed the CMMI Level 3 certification, upgraded the ISO certificate and at the same time improved the customer satisfaction index. This was reflected on the scorecard of the metrics to be presented to the Fortune 50 Company management for Q2 (Figure 4).

Figure 4 – ITWorx Top Supplier Metric for Q2 – 2010
Now, it was time to complete the remaining improvement tasks to achieve the required scores on the Top Suppliers program. This would cover the lean assessment category and specifically the factors related to 5S and Value Stream Management (VSM).
It was the time for the internal quarter review meeting between Reem and the implementation team. This regular meeting was held at the end of each quarter to discuss the progress in the Top Suppliers program and to prepare for the client review meeting that was attended by representatives from all related business units. The team had to prepare a presentation including the quarter results in the form of a scorecard which showed the current status of the four categories along with the details of the metrics for each of the business units. The presentation also showed the scorecard for the previous four quarters and the corresponding details.
What’s Next
According to the Top Suppliers implementation plan, activities related to Lean were due to start. Those activities were grouped into two projects which would focus on two factors of the lean assessment; 5S and Value Stream (Process) Management (VSM). By the end of the review meeting, the team would have reviewed the initial projects’ plans, agreed about the objectives and assigned team members for each project.
The objective of the first project was to implement 5S throughout the whole organization in both Cairo and Alexandria branches. Afaf Shiha, the Operations Manager, would lead the project activities and Dalia Anan, Quality Assurance Manager, would be the planning manager for the project. The initial plan was to divide the organization into areas, and to implement 5S to all those areas in phases (Exhibit 4). In each phase, the groups involved would first receive training on 5S concepts. The groups would then be required to apply the 5S concepts on their workplace within a specific period using tools like the red tags (Exhibit 5). The implementation team would then do regular audits to ensure process sustainability (Exhibit 6).
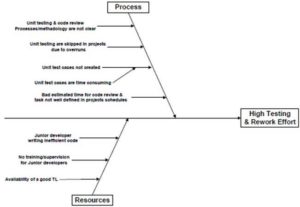
The objective of the second project was VSM using Six Sigma. Dahlia Arafa would lead this project. The plan was to get five team members certified in Six Sigma (one Black Belt and four Green Belt) where a certification project had to be implemented successfully using Six Sigma concepts. The chosen certification project would focus on implementing an effective code review and unit testing (Exhibit 7). The aim was to start the VSM with those processes and then use the same techniques with other processes. The six sigma implementation would follow the DMAIC methodology. Another important activity in the six sigma project was to spread the six sigma concepts awareness within ITWorx.
Conclusion
In the review meeting, Reem became aware of the progress achieved in the Top Suppliers program. She was comfortable with the work done in quality and delivery. As for the Customer Satisfaction, the progress that happened did not show yet, as the score is accumulated for the last four quarters. It required sustaining the good progress so when removing the under-performing quarters from the start the cumulative score would reach the target.
In lean assessment category, and for the two projects to be launched, Reem discussed the details of the proposed projects’ plans. She approved the approach of the two projects and their initial plans, and would proceed to request the required resources and budget for both projects.
Due to the tight deadline for the Fortune 50 Company contract renewal, Reem was anxious about getting things done on time. Although the current progress was promising, she was still worried about the outcome of the two new projects. The success of those projects was the cornerstone in achieving the remaining targets of the Top Suppliers Program. Reem started thinking if it was possible to get those projects done on time and what support was needed for the implementation team to achieve the required targets?
Exhibits
Exhibit 1 – ISO 9001:2000 Certificate

The certificate of the upgrade to ISO 9001:2008 is not yet received by ITWorx
Exhibit 2 – CMMI Level 3 Renewal
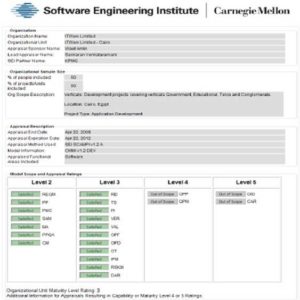
Extracted from http://sas.sei.cmu.edu/pars/pars_detail.aspx?a=12686 , accessed on October 2010
Exhibit 3 – ITWorx Partners (http://www.itworx.com/Showcase/Partners/- accessed on October 2010)

Exhibit 4 – 5S Project Proposed Plan
Exhibit 5 – 5S – Red Tag Label

Exhibit 6 – 5S Audit Checklist and Comments Sheet
Exhibit 7 – Six Sigma Certification Project – Define Phase Problem
Glossary
B
BEA
BEA Systems, Inc., a leading provider of enterprise application infrastructure solutions which was acquired by Oracle in 2008. The addition of BEA to is expected to accelerate innovation by bringing together two companies with a common vision of a modern service-oriented architecture (SOA) infrastructure and to further increase the value that Oracle delivers to its customers and partners. Together, Oracle and BEA provide a complementary best-in-class middleware portfolio that spans Java Application Servers, transaction processing monitors, SOA and business process management, user interaction and Web 2.0, identity management, business intelligence, enterprise content management and vertical-specific technologies. [source Oracle website]
Black Belt
Black Belt is a level of professional certification in Six Sigma. The Certified Six Sigma Black Belt is a professional who can explain Six Sigma philosophies and principles, including supporting systems and tools. A Black Belt should demonstrate team leadership, understand team dynamics and assign team member roles and responsibilities. Black Belts have a thorough understanding of all aspects of the DMAIC model in accordance with Six Sigma principles. They have basic knowledge of Lean enterprise concepts, are able to identify non-value-added elements and activities and are able to use specific tools. [source Global Voice of Quality – ASQ website]
C
CMMI
CMMI is a process improvement approach that provides organizations with the essential elements of effective processes that ultimately improve their performance. CMMI can be used to guide process improvement across a project, a division, or an entire organization. It helps integrate traditionally separate organizational functions, set process improvement goals and priorities, provide guidance for quality processes, and provide a point of reference for appraising current processes. [ source SEI website]
D
DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control)
DMAIC is a six sigma project methodology inspired by Deming’s Plan-Do-Check-Act cycle. Improvement teams use the DMAIC methodology to root out and eliminate the causes of defects:
D: Define a problem or improvement opportunity.
M: Measure process performance.
A: Analyze the process to determine the root causes of poor performance; determine whether the process can be improved or should be redesigned.
I: Improve the process by attacking root causes.
[source Global Voice of Quality – ASQ website]
G
Green Belt
The Six Sigma Green Belt operates in support of or under the supervision of a Six Sigma Black Belt, analyzes and solves quality problems and is involved in quality improvement projects. A Green Belt is someone with at least three years of work experience who wants to demonstrate his or her knowledge of Six Sigma tools and processes. [source Global Voice of Quality – ASQ website]
I
ISO
ISO (International Organization for Standardization) is the world’s largest developer and publisher of International Standards.
ISO is a network of the national standards institutes of 163 countries, one member per country, with a Central Secretariat in Geneva, Switzerland, that coordinates the system.
ISO is a non-governmental organization that forms a bridge between the public and private sectors. On the one hand, many of its member institutes are part of the governmental structure of their countries, or are mandated by their government. On the other hand, other members have their roots uniquely in the private sector, having been set up by national partnerships of industry associations. [source ISO website]
P
Plumtree
Plumtree Software, Inc. engages in the development, marketing, and sale of a suite of software products for deploying Web applications. The company’s Enterprise Web Suite combines portal, content management, collaboration, integration, and search technologies. Its Corporate Portal provides the framework for applications, supports virtual community workspaces, and integrates them into a cohesive Web work environment. The Collaboration Server enables people to work together via the Web, supporting tasks, projects, communities, calendars, discussions, and document sharing with version control. The Content Server enables publication and management of Web content for portals and Web applications, with forms-based publishing, branding, templates, workflow, approvals, and content expiration. The Search Server indexes and searches all the documents, information, applications, communities, discussions, Web sites, and other content accessible through the portal. The Studio Server provides tools to portal managers to create forms-based portlets and application components without coding. The Web Services Integration technologies connect the portal to enterprise systems, repositories, and resources, with support for both .NET and Java integration. It also offers development and administration tools that are used to assemble, customize, deploy, and manage applications for users inside and outside the enterprise. In addition, Plumtree Software offers deployment and support services, consulting services, and training classes. It markets and sells its products through its direct sales force and through systems integrators, value-added resellers, and original equipment manufacturers in the United States, Canada, Europe, and Asia Pacific. Plumtree Software, Inc. was founded in 1996 and is headquartered in San Francisco, California. Plumtree Software Inc. operates as a subsidiary of Oracle Corp. [source Businessweek investment website]
R
RRCA
Root cause analysis is a structured investigation that aims to identify the true cause of a problem and actions necessary to eliminate them.
[source Root Cause Analysis book]
Relentless Root Cause Analysis (RRCA) is a methodology for persistently performing root cause analysis to resolve root causes and to prevent the problem from recurring. RRCA find the fault in the process and not the person. Techniques to carry on RRCA include fishbone diagram and five why’s analysis.
S
5S
5S is based on Japanese words that begin with the letter ‘S’. The term “5S” references the five elements of this system: Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize and Sustain.
Sort (Seiri) – This first step is where we focus on removing all unnecessary items from the workplace. Basically, when in doubt, throw it out. An effective method of doing this is to red tag all items that are suspected of not being needed. Questions to be asked during the red tag event are is this needed, if it is needed, is this quantity necessary, if it is needed, does it need to be stored here? All of the tagged items are moved to a designated location marked red tag area where a person of authority determines the outcome of each item. Effective Sort implementation results in problems removed from the workflow, frees up workspace, and enhances productivity.
Set in Order (Seiton) – The second step of the 5S process focuses on efficient storage and location methods. In simplest terms “a place for everything and everything in its place”. Questions to be asked in this phase:
- What is needed to get the job done?
- Where should it be located?
- How many do I truly need?
To effectively set things in order you can use marking tape, labeling systems, bins, magnets, pouches, trash barrels, brooms, peg boards, clips, hangers and signs. The result of this process makes for a much more organized workplace where folks know exactly where to find what they need thus saving time and being more productive.
Shine (Seiso) – The third step focuses on cleaning up the place now that all the clutter and junk has been removed. Obviously one benefit of this step is to make the workplace cleaner and brighter where everyone will enjoy working. Another purpose is to keep everything working properly, so that it’s ready to be used when needed. Cleaning needs to become part of daily work habits which allows tools, equipment and work areas ready for use. The benefits of a clean work environment are; improved morale, defects become more obvious, improves safety by removing dust, oil and dirt and increases machine maintenance as daily inspections increase. On the last point, inspection occurs as a result of cleaning. One can’t help but inspect equipment or an area that they’re cleaning.
Standardize (Seiketsu) – By implementing the fourth step of 5S, Standardize, we make sure that the first three steps are maintained. By implementing standardization, we ensure that conditions prior to the first three activities won’t resurface. One means of standardizing is to use a 5S Chart to help track activities and define responsibilities. Concise maintenance schedules are another good tool for standardization.
Sustain (Sustain) – The fifth step in the 5S journey which is by far the most difficult where you need to make it habit to properly maintain the new processes. This is the critical step to keep the benefits of the previous four steps in place.
[source 5s Store website]
Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a fact-based, data-driven philosophy of quality improvement that values defect prevention over defect detection. It drives customer satisfaction and bottom-line results by reducing variation and waste, thereby promoting a competitive advantage. It applies anywhere variation and waste exist, and every employee should be involved.
In simple terms, Six Sigma quality performance means no more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities. [source Global Voice of Quality – ASQ website]
Standard Work
Standard work is a precise description of each work activity specifying cycle time, takt time, the work sequence of specific tasks, and the minimum inventory of parts on hand needed to conduct activity.
[source Lean Thinking book]
The target is to reach a repeatable way of doing work that is efficient and waste free. Continuous improvement is used to ensure that the standard work contains the best current practices known to deliver the highest quality.
T
Total Productive Maintenance (TPM)
A series of methods, originally pioneered by Nippondenso (a member of the Toyota group), to ensure that every machine in a production process is always able to perform its required tasks so that production is never interrupted.
[source Lean Thinking book]
V
Value Stream Management (VSM)
Value Stream Management is the method for creating a map of the existing processes and then sorting the included actions into categories: 1) those which actually create value as perceived by the customer; 2) those which create no value but are currently required by the product/service development and so can’t be eliminated just yet; and 3) those actions which don’t create value as perceived by the customer and so can be eliminated immediately.
Category 3 is eliminated first, and then category 2 is improved to create value as perceived by the customer. A value stream is a group of processes that delivers value to its customers. [source Lean Thinking book]
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
References
‘About ISO,’ International Organization for Standardization – ISO [Online], [Retrieved October 2010], http://www.iso.org/iso/about.htm
Publisher
Andersen, B. & Fagerhaug, T. (2006). Root Cause Analysis: Simplified Tools and Techniques, Second Edition, American Society for Quality, Quality Press, Milwaukee
Publisher
‘CMMI Overview?,’ Software Engineering Institute – SEI [Online], [Retrieved October 2010], http://www.sei.cmu.edu/cmmi
Publisher
ITWorx website [Online], [Retrieved October 2010], http://www.itworx.com
Publisher
James P. Womack & Daniel T. Jones (2003). Lean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation, Second Edition, Free Press, Avenue of the Americas, New York.
Publisher
‘Oracle and BEA Systems?,’ Oracle [Online], [Retrieved October 2010], http://www.oracle.com/bea/index.htm
Publisher
‘Plumtree Software,’ Business Week [Online], [Retrieved October 2010],
http://investing.businessweek.com/research/stocks/private/snapshot.asp?privcapId=33089
Publisher
‘Six Sigma Black Belt,’ The Global Voice of Quality – ASQ [Online], [Retrieved October 2010],
http://asq.org/certification/six-sigma
‘Six Sigma – The DMAIC Methodology,’ The Global Voice of Quality – ASQ [Online], [Retrieved October 2010],
http://asq.org/learn-about-quality/six-sigma/overview/dmaic.html
Publisher
‘Six Sigma,’ The Global Voice of Quality – ASQ [Online], [Retrieved October 2010],
http://asq.org/learn-about-quality/six-sigma/overview/overview.html
Publisher
‘What is 5S?,’ The 5S Store [Online], [Retrieved October 2010], http://www.the5sstore.com/whatis5s.html
Publisher


















