Introduction
Electronic commerce (abbrv. e-commerce) represents the activity of buying and selling goods or services using the internet, including the transfer of money to execute these transactions. The mentioned activities can be operated under all four main market segments: business to business, business to consumer, consumer to consumer and consumer to business.
Driven by an unprecedented event in recent history, e-commerce grew by over 30% in 2020, as many consumers were forced to adapt to online shopping (Hyder, 2020). As a result, companies such as Amazon or Walmart achieved great sales online, despite the pandemic situation. Companies that develop platforms dedicated to e-commerce felt the need of retailers to use online services, so they released improved versions of their products. It is still questionable if this consumer’s behaviour will become a habit, but will certainly be maintained at least in 2021.
Considering the Internet history, the lockdown came at a decent time for different industries. From an economic perspective the impact is huge, but only try to imagine having this outbreak 10 or 15 years ago. Euromonitor International reported that for the first time in history, in 2019 more than half of the population was connected to the internet, meaning that humanity had the necessary infrastructure for moving online (Evans, 2020). This paper uses both qualitative and quantitative research methods to present e-commerce along with its trends, benefits and potential challenges caused by technology, security and the ever-changing consumer preferences.
According to BuiltWith, in top three in e-commerce platforms’ usage, we can find: WooCommerce Checkout, with 3003043 websites (14.86%), Shopify with 1537580 websites (7.61%) and Win Stores with a total number of 1421492 websites (7.03%) (BuiltWith, 2021). Anticipating the necessity of powerful platforms, all those providers released new versions. Only WooCommerce released 10 new versions in 2020, from 4.0 to 4.9, offering innovative features like performing multiple tasks at the same time and an updated report system (LitExtension, 2021).
Mobile commerce (abbrv. m-commerce) is a form of electronic commerce which includes all the specific activities mentioned above, but they are performed using a portable device, such as a phone, a tablet or newer devices which are considered to be smart. The majority of the platforms that support e-commerce offer solutions for mobile devices, either optimized versions for browsers or applications that most of the time offer a better user experience. A fundamental feature of m-commerce is mobility, meaning that the information can be accessed at any time and from everywhere.
Business Model is a conceptual plan for generating profit, identifying the products or services that are intended to be sold, the targeted market and the anticipated costs. Regardless of the activity type, offline or online, a company must have a business model, a blueprint of their patronage. The online market comply with all the main business principles, so the traditional model will also work for them. Online environment created opportunities for new revenue models:
- Subscription and Licencing – the two models present lots of similarities, as being most popular among SaaS companies, ensuring recurring revenue. Usually, subscription plans are well defined, divided into specific categories (e.g. Free, Basic, Premium and Enterprise), starting from the one for which you have very limited data and going through versions that add more benefits. The main difference between subscriptions and licenses is that a subscription needs to be periodically renewed, while the licence runs until one of the parties involved decides to terminate it (Campbell, 2019).
- Markup – companies buy products, add a percentage to the initial price of it and sell it again, making a profit margin on the original purchase. This model is used by mediators e-commerce marketplaces, such as Amazon who charges 15% the sellers who use the website (Campbell, 2019). One of the most common examples is buying products from low rated websites, adding a private label and selling it on premium sites, like Amazon FBA, eBay or Etsy. They will pack, ship and provide customer service for the goods.
- Advertising and Donations – depending on their traffic, websites receive money from different companies to add advertisements on their pages on certain corners, generating constant revenue. Other nonprofit organizations rely on the donations of regular users (Campbell, 2019).
- Affiliate – similar to the classic way, in which a middleman is charging commision for each transaction that happens between two parties. Most on social media, goods or links are promoted depending on how convincing the person was, generating revenue for the company and an income for the middleman.
Online shopping is one of the most popular activities worldwide and from a financial perspective, is expected to grow even more. In 2020, retail e-commerce sales amounted to 4206 billion US dollars and projected to grow up to $6542 billion (Statista, 2020). This statistic includes purchases done via the internet, regardless of the device and method of payment.
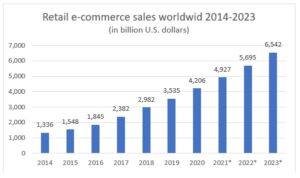
Fig 1. Retail online sales 2014-2023 (data source: (Statista, 2020), *Forecast)
E-Commerce Trends among Advantages and Disadvantages
Covid-19 had a substantial impact over consumers’ shopping habits and people are forced to change their purchasing behavior. The difficulties come from trying to distinguish the trends generated by the reactions of Covid-19 and the real ones dictated by the information technology evolution. It might be that the lockdown made the technologies of the future come earlier into our lives.
- Artificial Intelligence – Mathematician Alan Turing changed IT history when he proved that computers can think (Copeland, 1998). More specifically they can simulate human intelligence; they can learn and adapt to new data without being assisted by humans. When it comes to e-commerce, organizations are using AI to predict and automate processes and practices. Customers are showing willingness to receive recommendations based on their previous shopping carts or on their internet searches. Sellers can see financial benefits on investing in AI, so by the end of 2022 the amount spent on AI research and implementation can reach $7.3 billion (LitExtension, 2021).
Chatbots are considered to be an important part of AI, as 53% of customers are more likely to buy from an online store where they can message to someone and 69% of them prefer chatbots for giving instantaneous responses. Due to their beneficial impact over company turnover, chatbots are most commonly used for sales (41%), customer support (37%) and marketing (17%) (FinancesOnline, 2020).
- Virtual Commerce using AR – Augmented Reality is an interactive version of real world enhanced by computer generated perceptual information, using digital sensory stimuli such as visual elements and sounds. First introduced in 1990, AR had been used in e-commerce since 2016 and completely changed the overall online shopping experience (LitExtension, 2021).
As people are getting more and more interest in technology, AR is rapidly becoming a trend. CEO of Threekit, Matt Gorniak, sees the pandemic as a unique opportunity to change behaviors and embrace the new way of buying. Considering that people’s expectations are increasing rapidly when it comes to technology, even after the pandemic, they will want better visual experiences, so in order to remain competitive on their markets, companies should invest in AR. According to the studies, visual images can increase consumer engagement by 66% in contrast with the traditional images (LitExtension, 2021).
Many companies foresaw the benefits of AR and implemented it. Whether we talk about the fashion industry, cosmetics, furniture or automotive, from Sephora to Ikea, from Gucci to Toyota, they are already leveraging the power of Augmented Reality.
- Buy Now, Pay Later – BNPL products are considered to be an alternative to credit cards and have expanded their popularity during the pandemic, as people turned to online shopping. They offer purchase flexibility for customers, buying whenever they want and paying later according to a payment schedule. By following the schedule, consumers will not have to pay any fee or interest.
Due to lockdown restrictions, purchasing activities moved over the internet and companies found new opportunities in increasing their incomes, by offering payment flexibility to customers. One of the biggest competitors on the e-commerce market, Amazon, started a partnership with Citi, allowing Citi card users to choose from a variety of payment plans (three, six, 12 and 48 months) (PYMNTS.com, 2020).
“Pay in 4” is a product from PayPal which offers the possibility to split the invoice in 4 payment transactions, one every two weeks, with no interest (PayPal, 2020).
Another sector of BNPL is defined by payment applications like Klarna, Afterpay and Clearpay which offer similar services, buying online products and paying them later according to a predefined schedule. According to Financial Times, this service can become harmful and raise concerns that people might be encouraged to buy more than they can afford, reaching the inability to pay (Cook, 2021). Considered to be an unregulated sector, compared with the main rival, credit cards, the Financial Conduct Authority launched a review in Great Britain in September 2020 over the unsecured credit markets, focusing on BNPL, in order to determine the impact over the consumer’s budget. Even the biggest player on the market, Klarna, emphasizes the need of stronger regulations. Through the U.K. lead, Alex Marsh, they declared that “Regulation has not kept up with innovation and the changes in consumer behavior. That’s why we fully support appropriate regulation which meaningfully improves consumer outcomes.” (Cook, 2021).
- Free Shipping – 90% of customers say that free shipping is the first incentive to shop online, while orders with free shipping average around 30% higher in value (Rudolph, 2017). Around 61% of consumers are tempted to cancel their purchase because of the extra shipping costs, according to Business2Community website (Rudolph, 2017).
Online stores know how to maintain their profits so they are using several ways by which customers pay for the shipping service without realizing it. Most of the time, the prices are increased, including the cost of shipping or they set a minimum spend threshold (LitExtension, 2021).
- Free returns – In close relationship with the shipping part of online purchasing, are found the returns, since more than 30% of the products ordered online are returned and 79% of consumers want free return shipping. In comparison, only 8.89% of the items bought in physical stores are given back (Saleh, 2019). The majority of people check the returns policy before placing an online order and if any costs are involved, they may decide to cancel the shopping cart.
According to (Saleh, 2019), free shipping and free returns are the most important features that influence the buyer’s decision.
- Sustainability – Covid-19 made people pay more attention to their health and to the environment, choosing sustainable products whenever they had the chance to choose. 87% of people would buy a friendly environment product, meaning that sustainability will drive safety for the upcoming years(LitExtension, 2021). Social responsibility is encouraged by large organizations, offering products made from recycled materials, organic food and electric cars.
- Social Platforms – Social Media crossed the borders of being a way in which people can interact with others, becoming a marketing tool. Social commerce is a trend which allows customers to discover brands or products that normally would not be part of their online searches. Social Platforms like Facebook and Instagram can now be used as an e-commerce platform; through Facebook Marketplace and Instagram Checkout, the final consumer can directly buy what they see in the commercials that appear on their walls. The new social platform, TikTok, made a partnership with Shopify which enabled Shopify sellers to connect to a TikTok business account and TikToK users to the store (LitExtension, 2021). This way the application can become a serious rival for Facebook.
Every good or service has to be paid, regardless of the method used for purchasing it. This pandemic changed not only the way in which we buy, but also the way in which we pay. In 2019, digital and mobile wallets accounted for 41.8 percent of global e-commerce payment transactions, making it the most popular method. By 2023, the hierarchy might change, but not the top two positions. It is expected that bank transfer overcomes debit cards and BNPL wins one position, substituting cash on delivery (Statista, 2020).
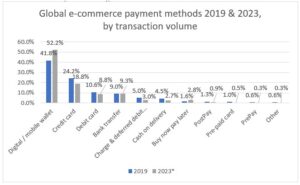
Fig 2. Global e-commerce payment methods (data source: (Statista, 2020), *Forecast)
Electronic commerce helped many businesses to become viable and profitable, but at the same time created new obstacles and some companies were not able to get through them. Like all business models, e-commerce comes with advantages and disadvantages which in this case can be analyzed from a double perspective using qualitative data, from consumers’ point of view and from the organizations part. Some of them might affect both parties involved in the selling process.
Table 1: Advantages of e-commerce, double approach
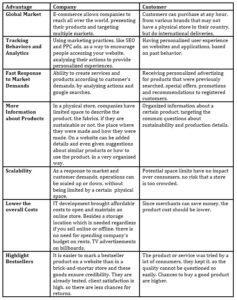
The benefits of electronic commerce are easily visible from both financial perspectives and targeted markets. During the lockdown, it was the only way to make supplies for most consumers, but from an analytical perspective, the disadvantages must be stated.
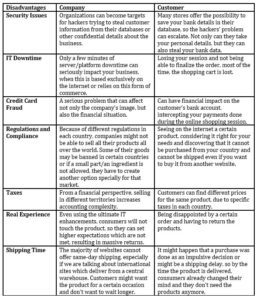
Table 2: Disadvantages on e-commerce, double approach
Data Protection and Security
Privacy and security in the IT systems is a continuous topic among the Data Protection Organizations, but also among the users. E-commerce can generate tremendous privacy issues and threats of security. Maintenance of users’ privacy must be a top priority for online platforms that offer these services, because if a user loses their trust, they lose a client. Technical methods for capturing clients’ data like cookies have been raising serious privacy issues and today each website requests visitor’s acceptance for cookies policy.
Adopted in April 2016, GDPR created rules for how European residents’ data must be managed, offering confidence and protecting users inside the EU. With a great impact over data handling, pertaining to different domains, from financial records, internet activity to medical history, organizations must be sure that they meet all the requirements of GDPR when creating an e-commerce platform. When accessing a website, the user must be notified about data collection within the GDPR rules, providing visibility to data protection policy, cookies policy and legal aspects of products and services (European Commision, 2019). Personal data can be anything from email, photos and IP addresses or any other customer information that makes it possible to identify an individual. Regardless of company location, an organization has to be compliant with the rules of collecting and storing personal data of anyone residing in the EU.
In less than two years, the number of data breaches increased with over 60% inside the EU or even doubled for certain countries (Statista, 2021). Netherlands maintained first position, with the highest number of cases, followed by Germany and the United Kingdom. At the opposite pole is Liechtenstein with a constant number of 15 cases. For Iceland, the security breach number of cases has increased more than 12 times (from 25 cases to 313), having the highest growth rate in Europe (Statista, 2021).
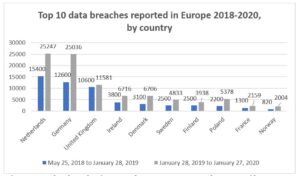
Fig 3. Top 10 data breaches in Europe between 2018 – 2020, by country (data source: (Statista, 2021))
Cyber security is a top priority not only for the European Union, but for countries all over the world. For fiscal year 2021, the U.S. government proposed a $18.78 billion budget for enhancing the security of critical infrastructure and important technologies (Statista, 2021). While digitization increased, corporations have had difficult times in remaining secure and the number of data breaches in the United States increased from 157 million in 2005 to 1.47 billion in 2019 (Statista, 2021).
The most common type of data breach is identity theft (Statista, 2018) and the larger consumer data breach of all time was done in 2014, but revealed only in 2016, when Yahoo was hacked (Statista, 2021). Most of the time, e-commerce involves financial transactions via the Internet, this part being extremely exposed to security issues. Financial access data theft is the third most common type of data breach, accounting for 13% of all data breaches (Statista, 2021).
There are rules and regulations applicable worldwide, which bring restrictions on different markets. Obstacles may lie ahead of any business and the majority of them reflect in the final cost of selling goods on the internet. In the top of the list can be found the taxes restrictions, as every state and country have different ways of calculating taxes and different percentages. Before displaying the final sale price on the website, organizations must consider the targeted markets. In some geographical zones, like the U.S., customers are used to seeing the prices without taxes, but in Europe or Australia, clients are accustomed to seeing the overall price. Depending on the item category, Great Britain applies VAT to all non-essential goods, while other countries have different percentages defined for VAT. In California for example, items that are sold in plastic bottles will carry an extra $0.11 recycling fee (Estay, 2020). Other limitations may include shipping and age restrictions. For certain products like alcohol, cigarettes, perfumes, perishables extra paperwork and fees are applicable, while some of them cannot be sold to children under certain ages.
Online payments need to accomplish one crucial standard, PCI DSS, not only for being compliant with the Security Standards Council, but also for gaining customers’ confidence, ensuring them that online sellers have the required processes and practices to prevent data breaches.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the brick-and-mortar business evolved over the years to online commerce, but it really became a necessity in 2020, when humanity has experienced an unprecedented situation in recent history. E-commerce comes with considerable benefits, but has its own risks and limitations. Overall changes are needed in a company’s business strategy, in order to align with the new trends and requirements. The maintenance costs for the physical locations may decrease, by closing shops or renting smaller spaces. But e-commerce involves other costs like platform license, website maintenance and security expenses.
Having analyzed the current technical data about e-commerce, we can conclude that open-source platforms are preferred by the customers and the most popular platform in 2021 will still be WooCommerce. M-commerce, as a subset of e-commerce, gains an important place on the market by offering flexibility and mobility. Different payment technologies bring value to online commerce and this is a major growth factor for e-commerce.
We have enough data to observe trends and growth paths for e-commerce, and artificial intelligence together with augmented reality are major functions that highlight a business. Using the latest technologies gives people confidence. Customers prefer to be sure about their purchase, so giving them as many details as possible and even being able to try online a certain item, like a piece of clothes or furniture, increases the customer loyalty degree.
One major test of an e-commerce platform is the online payment method. People become skeptical when they have to provide access to their financial data and to use their credit card information. A preferred method would be cash on delivery, but due to cash limitations generated by the 2020 outbreak, this trend seems to be changing. Probably, the most important drawback of e-commerce is the lack of human interaction and is expected at the end of the actual pandemic to have a small slowdown in popularity. Experts predict that people might feel the need of going out, socializing and returning to old habits for a certain period of time, meaning that they would prefer to go to physical stores for their day-to-day groceries.
Privacy and security are emerging issues in electronic commerce. This paper presents the main idea about these problems and the incredible way in which the data breaches cases increased in a short time. Privacy is considered a growing public issue, as some organizations or hackers are still able to find different ways to violate some limits without major consequences. In the end of the study, as a limitation, I would mention the fact that this paper presents general information about data protection and its issues, without offering a well-defined methodology on how to avoid data breaches.
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
References
- BuiltWith, 2021. eCommerce Usage Distribution on the Entire Internet. [Online]
- Available at: https://trends.builtwith.com/shop/traffic/Entire-Internet
- Campbell, P., 2019. What is a Revenue Model? 11 Types of Revenue Models You Can Use. [Online]
- Available at: https://www.profitwell.com/recur/all/11-popular-types-of-revenue-models-used-today
- Cook, L., 2021. Time to tighten rules on ‘buy now pay later’ operators. [Online]
- Available at: https://www.ft.com/content/9ff96a25-d340-46fe-be5d-197cb4a7ffa7
- Copeland, B. P., 1998. Alan Turing – British mathematician and logician. [Online]
- Available at: https://www.britannica.com/biography/Alan-Turing#ref214879
- Estay, B., 2020. 10 Online Business Laws You Need to Know for Internet Selling. [Online]
- Available at: https://www.bigcommerce.com/blog/online-business-laws/
- European Commision, 2019. Legal regulations for e-commerce. [Online]
- Available at: https://ec.europa.eu/growth/sectors/tourism/business-portal/understanding-legislation/legal-regulations-e-commerce_en
- Evans, M., 2020. 5 Ways Tech Will Change Commerce in 2020. [Online]
- Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/michelleevans1/2020/01/22/5-ways-tech-will-change-commerce-in-2020/?sh=43621ae1441c
- FinancesOnline, 2020. 86 Critical Chatbot Statistics: 2020/2021 Data Analysis & Market Share. [Online]
- Available at: https://financesonline.com/chatbot-statistics/
- Hyder, S., 2020. 3 E-Commerce Trends To Watch In 2021. [Online]
- Available at: https://www.forbes.com/sites/shamahyder/2021/12/29/3-ecommerce-trends-to-watch-in-2021/?sh=66e0f8146719
- LitExtension, 2021. E-Commerce in 2021: Top Platforms Report & Prediction and Industry Trends. [Online]
- Available at: https://litextension.com/ecommerce-trends-2021-top-platforms.html
- PayPal, 2020. Now you can Pay in 4 with PayPal. [Online]
- Available at: https://www.paypal.com/us/for-you/pay-in-4?_gl=1*5qiew6*_gcl_aw*R0NMLjE2MTI3MDgxMzIuQ2owS0NRaUF2UDZBQmhDakFSSXNBSDM3cmJTeHhTM1BJcHNGd0xpU0YtN2VmZDJlOUtjTVFtVlFqSGFhTG1zWmlITDg2Tkh5TG0tM1AzRWFBaDNDRUFMd193Y0I.&_ga=2.97070175.1743096786.1613410794-195255521
- com, 2020. Citi BNPL Option Now in Amazon. [Online]
- Available at: https://www.pymnts.com/buy-now-pay-later/2020/citi-bnpl-option-now-on-amazon/
- Rudolph, S., 2017. Does Free Shipping Influence Online Buying Decisions [Infographic]. [Online]
- Available at: https://www.business2community.com/infographics/free-shipping-influence-online-buying-decisions-infographic-01752462
- Saleh, K., 2019. E-commerce Product Return Rate – Statistics and Trends [Infographic]. [Online]
- Available at: https://www.invespcro.com/blog/ecommerce-product-return-rate-statistics/
- Statista, 2018. Distribution of global data breach incidents in 1st half 2018, by type. [Online]
- Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/329593/frequency-share-incident-classifiaction-patterns/
- Statista, 2020. Global e-commerce payment methods 2019 & 2023, by share of transaction volume. [Online]
- Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1111233/payment-method-usage-transaction-volume-share-worldwide/
- Statista, 2020. Retail e-commerce sales worldwide from 2014 to 2023. [Online]
- Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/379046/worldwide-retail-e-commerce-sales/
- Statista, 2021. Number of compromised data records in selected data breaches as of April 2020. [Online]
- Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/290525/cyber-crime-biggest-online-data-breaches-worldwide/
- Statista, 2021. Number of data breaches reported in Europe 2018-2020, by country. [Online]
- Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/996456/data-breaches-reported-in-europe-by-country/
- Statista, 2021. Proposed budget of the U.S. government: proposed cyber security spending in FY 2017-2021. [Online]
- Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/675399/us-government-spending-cyber-security/







